Function: The engine is the primary source of mechanical energy in the generator. It burns fuel (diesel, natural gas, propane, etc.) to produce the rotational force required for electricity generation.
Key Parts:
- Fuel System: Includes the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel injector, and filters. It supplies fuel to the engine.
- Cooling System: Ensures the engine doesn’t overheat, typically using a radiator and cooling fan.
- Exhaust System: Removes combustion gases from the engine (exhaust pipes, mufflers).

Function: Converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. The alternator consists of a rotor and a stator that produce alternating current (AC) electricity.
Key Parts:
- Rotor: A rotating magnetic field inside the alternator.
- Stator: A set of windings where electricity is induced by the rotating magnetic field.
- Bearings: Support the rotating components and reduce friction.
Function: Controls and maintains the output voltage of the generator at a consistent level.
Key Parts:
- Exciter Windings: Supplies current to the rotor to create a magnetic field.
- Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR): Adjusts the excitation current to stabilize output voltage under varying loads.
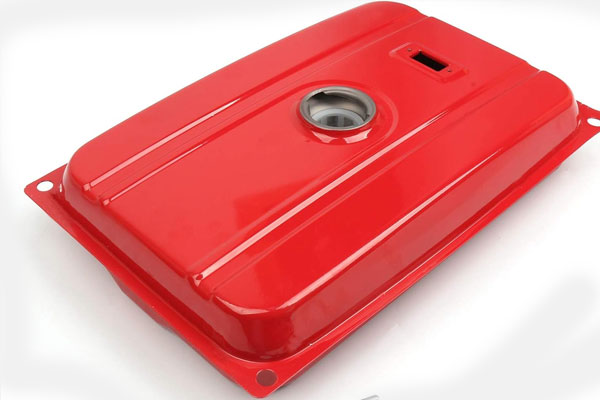

Function: Supplies fuel to the engine and regulates fuel flow for combustion.
Key Parts:
- Fuel Tank: Stores the fuel required for running the generator.
- Fuel Pump: Delivers fuel from the tank to the engine.
- Fuel Filter: Removes impurities from the fuel before it enters the engine.
- Fuel Injector: Delivers fuel into the combustion chamber of the engine.
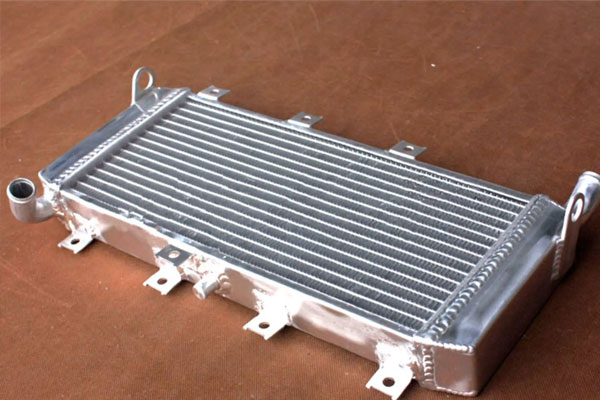

Function: Maintains the optimal operating temperature of the engine and other generator components by removing excess heat.
Key Parts:
- Radiator: Uses a fan to dissipate heat generated by the engine.
- Coolant: Circulates through the engine to absorb and remove heat.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant within the system.
- Thermostat: Controls the flow of coolant based on temperature.
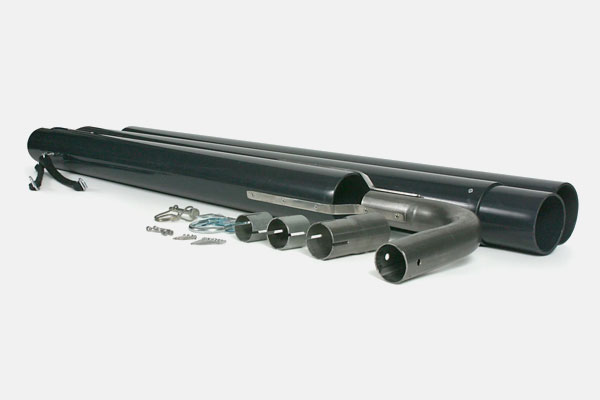

Function: Directs and removes harmful exhaust gases from the generator.
Key Parts:
- Exhaust Pipe: Channels combustion gases out of the engine.
- Muffler: Reduces noise produced by the engine during combustion.
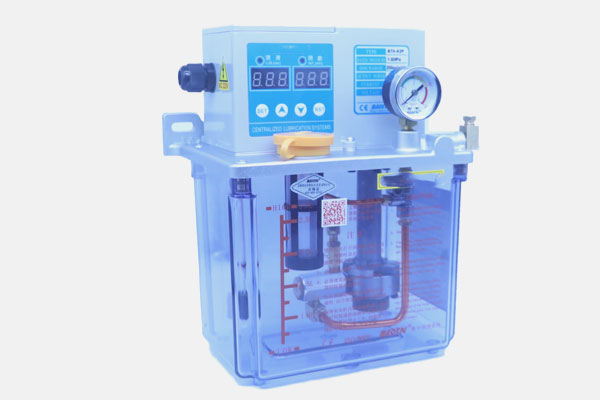

Function: Ensures smooth operation of moving parts inside the engine by reducing friction.
Key Parts:
- Oil Pump: Circulates oil to lubricate engine components.
- Oil Filter: Removes contaminants from the oil to prolong engine life.
- Oil Pan: Stores the lubricating oil at the base of the engine.
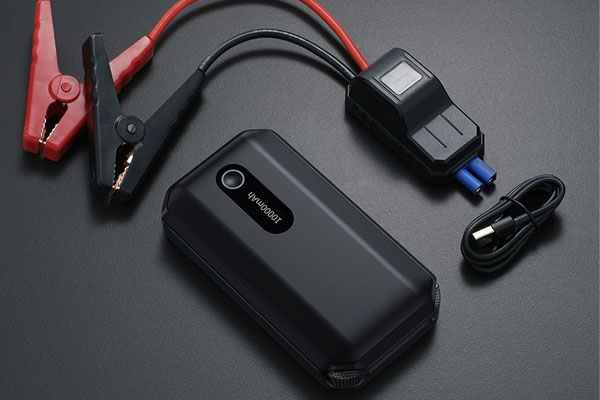

Function: Provides the initial electrical energy required to start the generator’s engine.
Key Parts:
- Starter Motor: Engages the engine’s crankshaft for ignition.
- Battery: Provides power to the starter motor.
- Battery Charger: Maintains the charge of the battery while the generator is not in use.
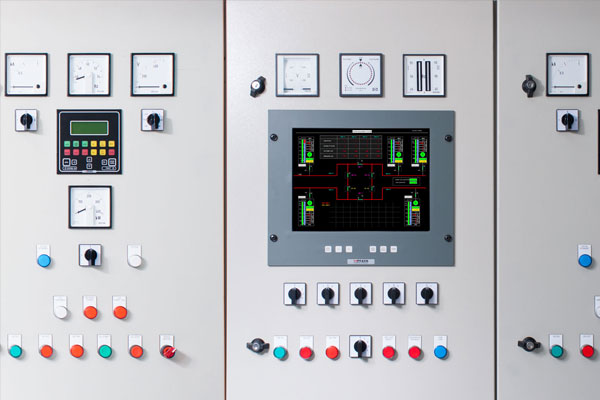

Function: The user interface that allows monitoring and controlling the generator’s operations.
Key Features:
- Start/Stop Buttons: Turns the generator on or off.
- Display Panel: Shows vital information such as voltage, frequency, running hours, fuel level, and temperature.
- Circuit Breaker: Protects the generator from overloading and short circuits.
- Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS): Automatically switches to generator power when the main power fails and back when the main power returns.

Function: The physical structure that supports the engine, alternator, and other components.
Key Parts:
- Vibration Mounts: Isolate vibrations from the generator to minimize noise and wear on components.
- Enclosure (Optional): Protects the generator from weather, dust, and external damage, especially in outdoor applications.
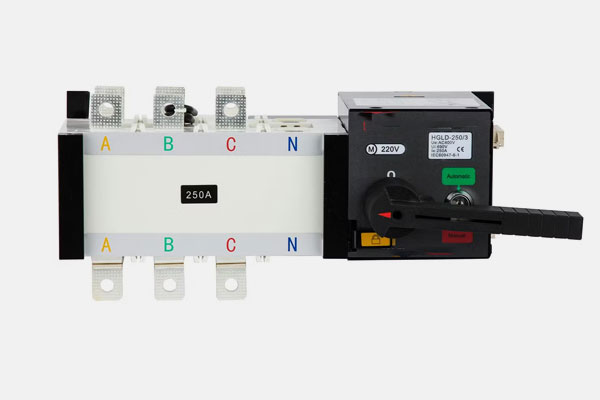

Function: Automatically switches the load from the main power supply to the generator in the event of a power failure.
Key Features:
- Detects loss of power and starts the generator automatically.
- Switches back to the main power when it is restored.
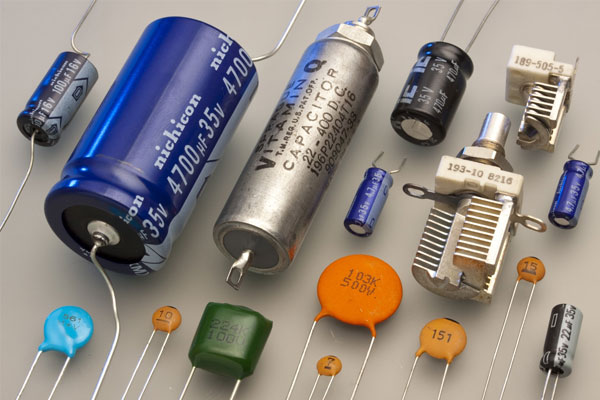

Function: In smaller generators, a capacitor can be used in place of the AVR to regulate voltage output.
Additional Components in Specialized Generators
Function: In steam or gas turbine generators, the turbine is driven by steam or gas pressure to turn the generator’s rotor.
Key Parts:
Blades: The vanes or blades of the turbine spin when subjected to high-pressure steam or gas.
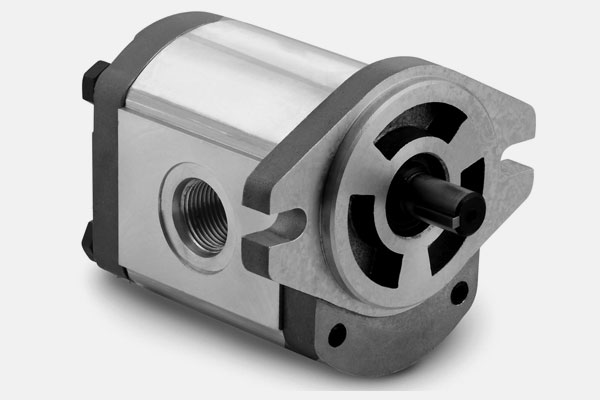

Function: In hydroelectric generators, water flow drives the hydraulic pump, which turns the turbine and generates electricity.
Common Generator Accessories
Fuel Level Sensors: Monitor the amount of fuel in the tank and trigger alerts when refueling is needed.
Heaters: Prevents the generator from freezing in cold environments.
Soundproofing Kits: Reduce noise from the engine, often required for residential or urban installations.
Remote Monitoring Systems: Allows real-time monitoring of generator performance from a distance using wireless networks or the internet.
Generator Maintenance Parts
To keep generators running efficiently, regular maintenance and replacement of certain parts are necessary:
Oil Filters: Should be replaced periodically to ensure smooth lubrication.
Air Filters: Prevent dust and debris from entering the engine.
Spark Plugs: Used in gas-powered generators, these need to be replaced after a certain number of operating hours.
Belts and Hoses: These wear out over time and need regular inspection and replacement.
