Instrumentation systems monitor and control key process variables
like pressure, temperature, flow, and level within industrial facilities. Essential components include:
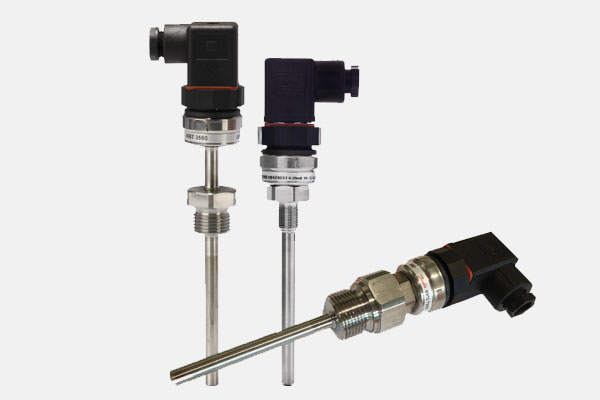

Function: Detect and transmit data on process parameters.
Examples: Pressure transmitters, temperature sensors (RTDs, thermocouples), flow transmitters (ultrasonic, magnetic), level sensors (radar, ultrasonic).
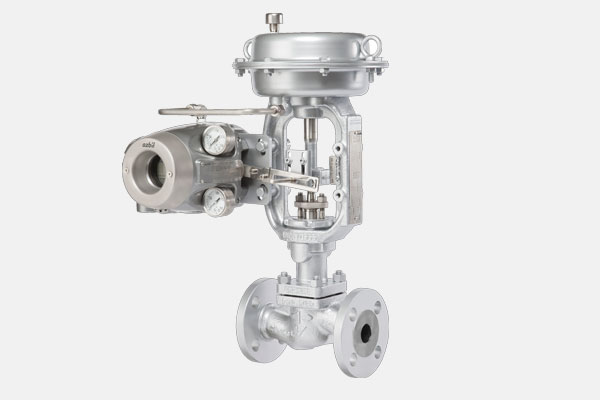

Function: Regulate fluid or gas flow within a process.
Examples: Globe, ball, butterfly valves; electric and pneumatic actuators.
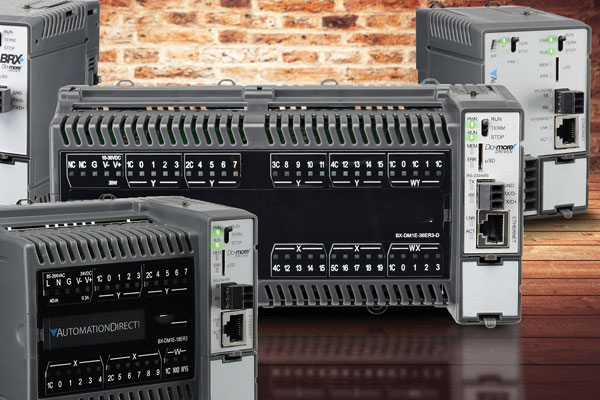

Function: Automate control of industrial processes.
Examples: Allen-Bradley PLCs, Siemens S7 series PLCs.

Function: Centralize control for complex processes.
Examples: Honeywell Experion, Emerson DeltaV.

Function: Allow operators to interact with control systems.
Examples: Touchscreen panels, graphical displays.
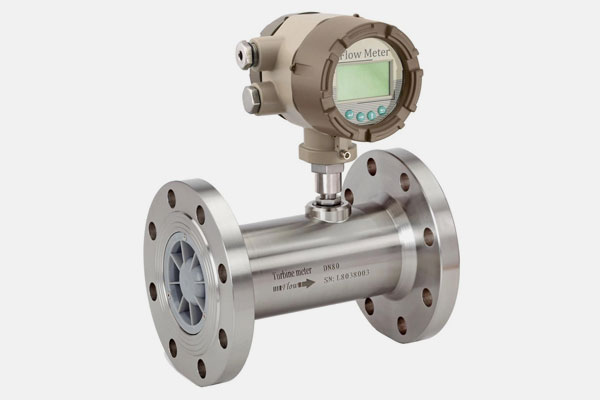

Function: Measure the flow rate of liquids or gases.
Examples: Turbine, Coriolis, electromagnetic flow meters.
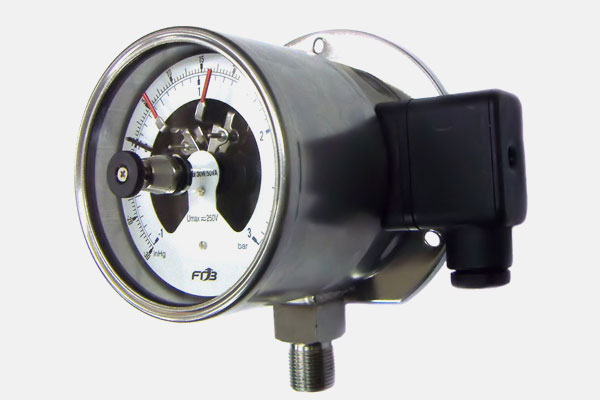

Function: Monitor and measure system pressure.
Examples: Bourdon tube gauges, diaphragm switches.
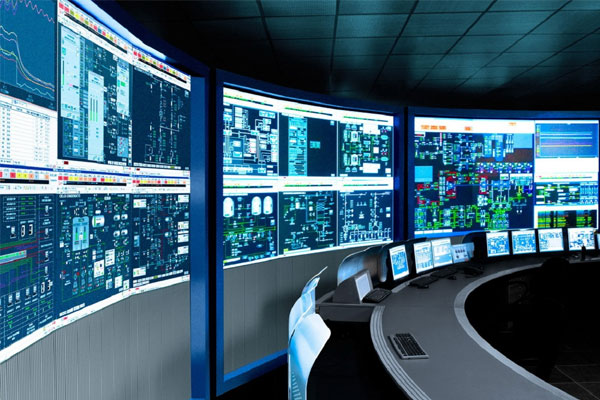

Function: Oversee and control plant processes.
Examples: SCADA systems, emergency shutdown (ESD), fire and gas detection systems.
Function: Control processes and devices based on set conditions.
Examples: Time delay relays, safety relays, temperature controllers.
Function: Ensure instrument accuracy.
Examples: Pressure calibrators, loop calibrators, temperature baths.
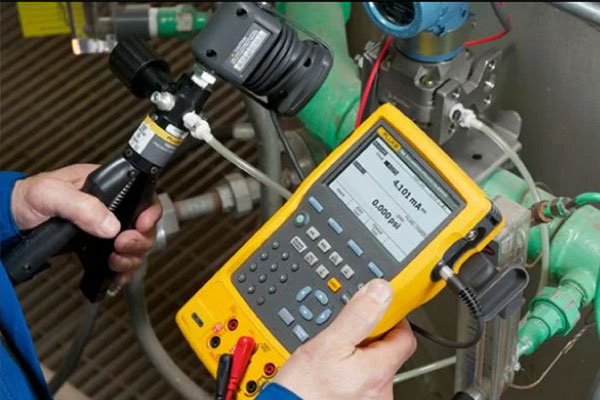

Function: Monitor conditions in remote or hazardous areas.
Examples: Vibration sensors, humidity sensors, gas detectors.

Function: Convert or isolate signals to ensure compatibility with control systems.
Examples: 4-20 mA to 0-10 V converters, isolated signal amplifiers.
