Mechanical Components
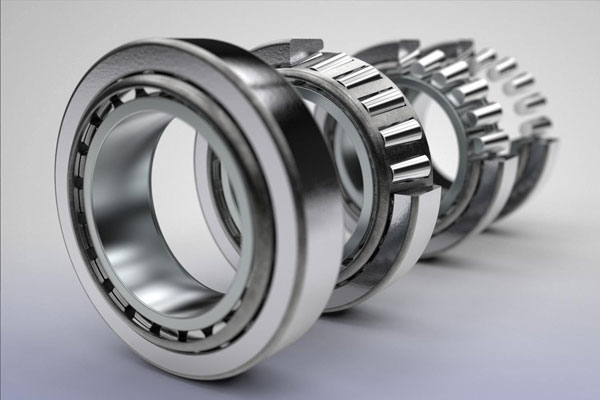

Bearings
Reduce friction between moving parts in machinery.
Types include ball bearings, roller bearings, and thrust bearings.
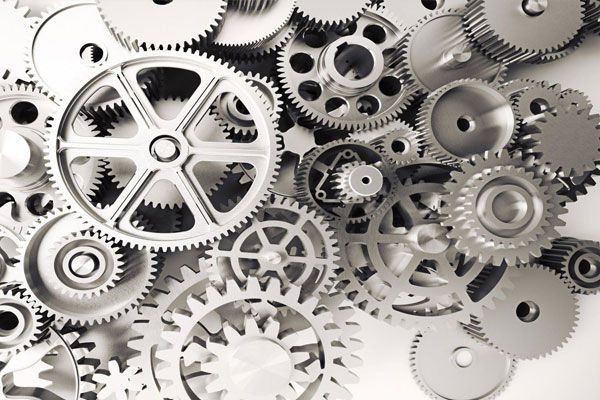

Gears
Transfer motion and torque between different machine parts.
Types include spur gears, bevel gears, and worm gears.
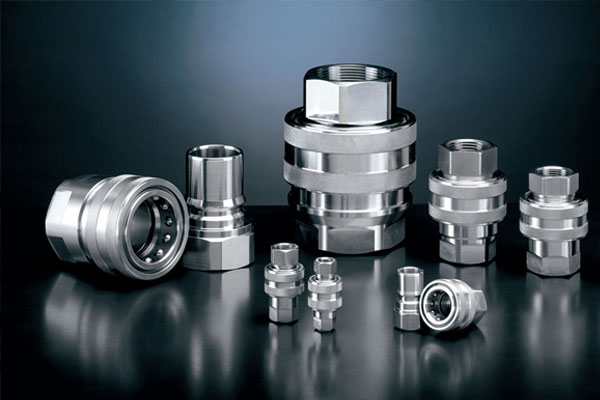

Couplings
Connect two shafts to transmit power while accommodating misalignment.
Types include rigid couplings, flexible couplings, and universal joints.
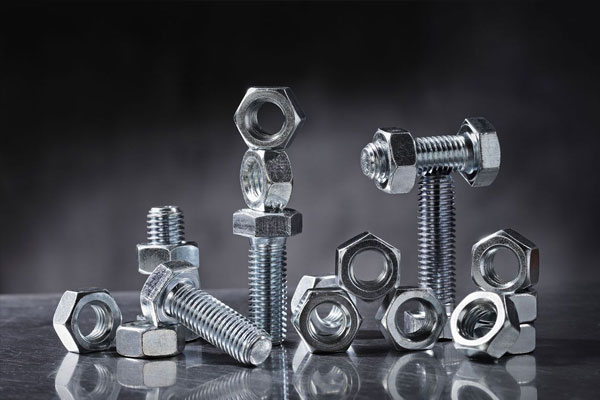

Fasteners
Essential for assembling machinery and structures, including bolts, screws, nuts, and washers.
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Components
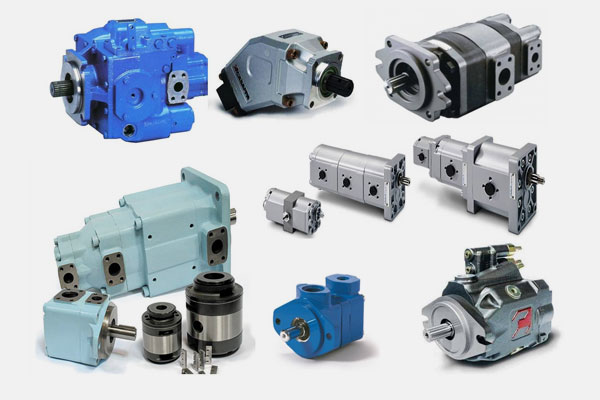

Hydraulic Pumps
Convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy to power systems.
Types include gear pumps, vane pumps, and piston pumps.
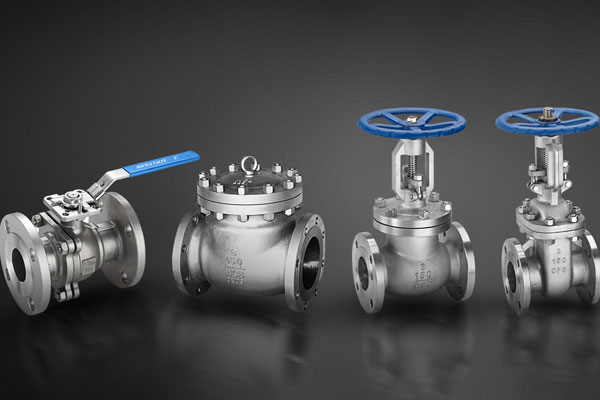

Valves
Control the flow and pressure of fluids in hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
Types include ball valves, check valves, and solenoid valves.
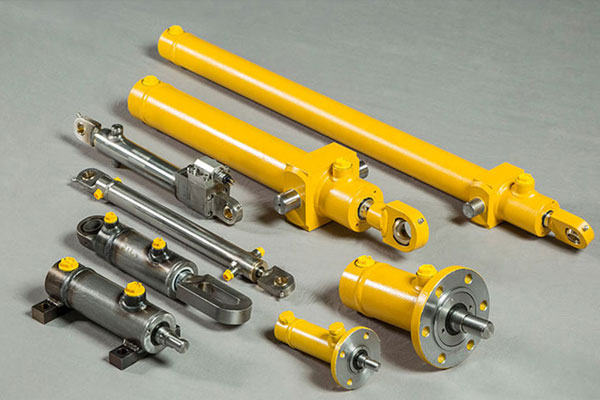

Cylinders
Convert hydraulic or pneumatic pressure into linear motion.
Types include double-acting cylinders and single-acting cylinders.
Electrical Components
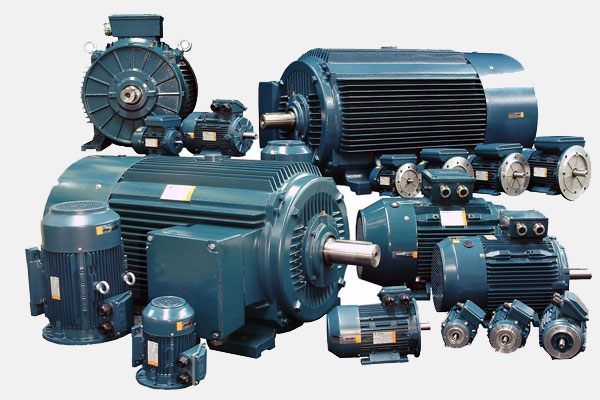

Motors
Convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Types include AC motors, DC motors, and stepper motors.
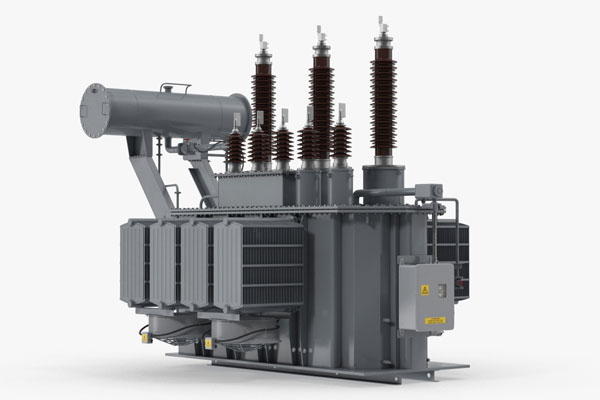
Transformers
Transfer electrical energy between circuits by stepping up or stepping down voltage.
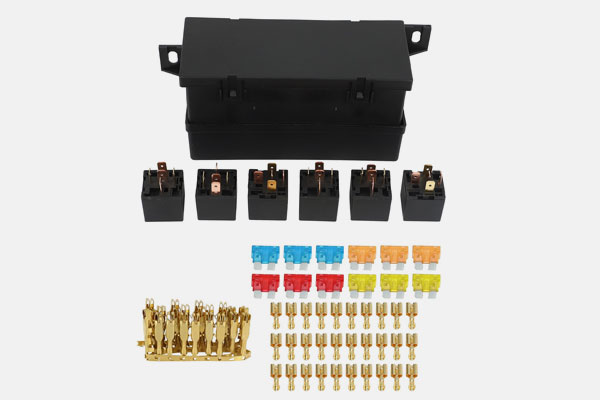

Switches and Relays
Control the flow of electricity in circuits.
Types include toggle switches, push-button switches, and contact relays.
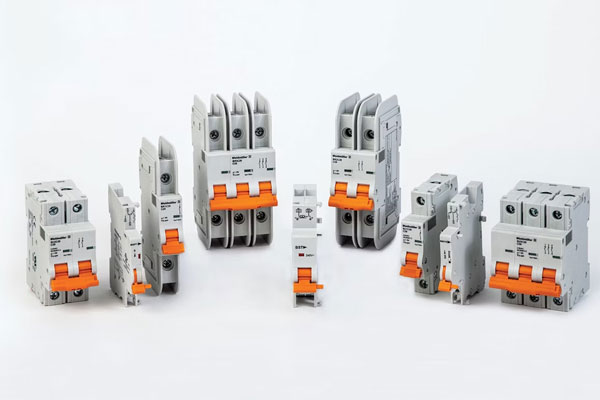

Circuit Breakers
Protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits.
Instrumentation and Control Parts
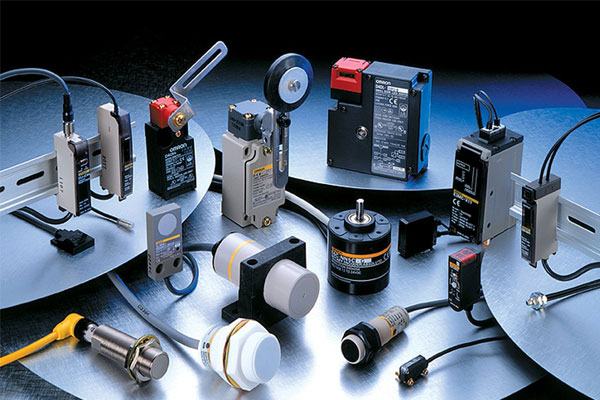

Sensors
Detect physical properties such as temperature, pressure, and flow.
Types include temperature sensors, pressure sensors, and flow meters.
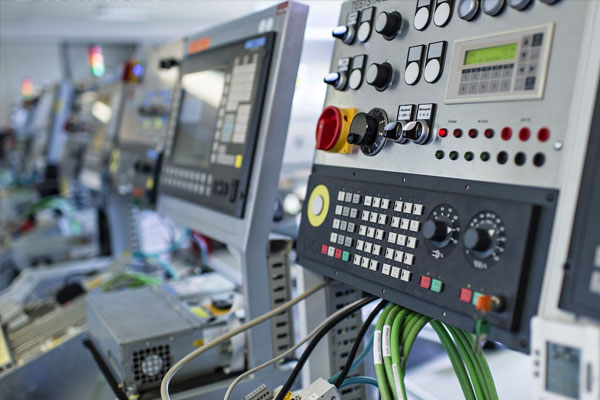

Controllers
Devices that regulate machinery operation based on sensor input.
Types include programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and distributed control systems (DCS).
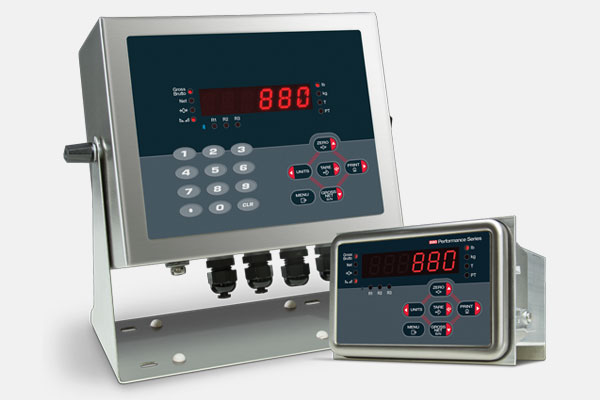

Displays and Indicators
Provide visual feedback about system status and performance.
Types include digital displays, analog gauges, and LED indicators.
Industrial Pumps
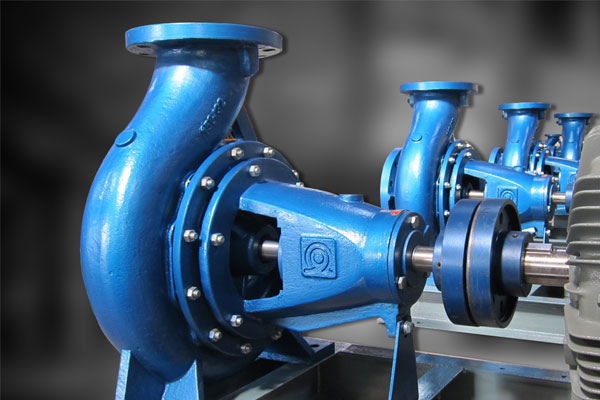

Centrifugal Pumps
Move fluids by converting rotational kinetic energy into hydrodynamic energy.
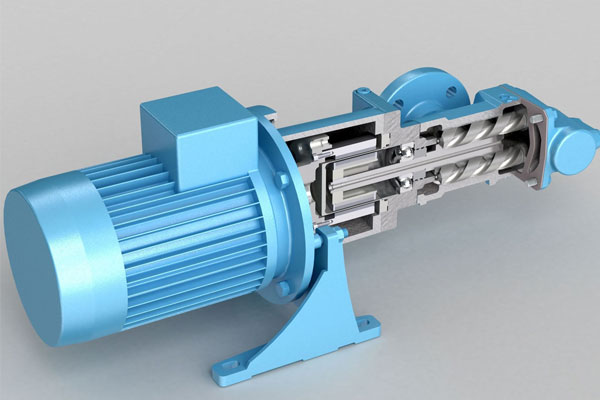
Positive Displacement Pumps
Move fluids by trapping a fixed amount and forcing it through the discharge.
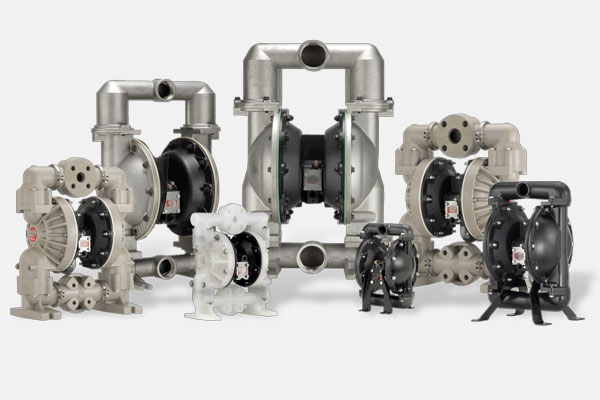

Diaphragm Pumps
Utilize a diaphragm to move fluids, making them suitable for corrosive or viscous liquids.
Conveyor Systems
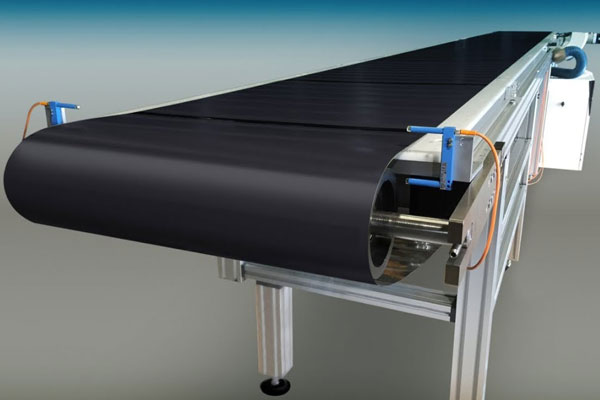

Belt Conveyors
Transport materials from one location to another using a continuous belt.
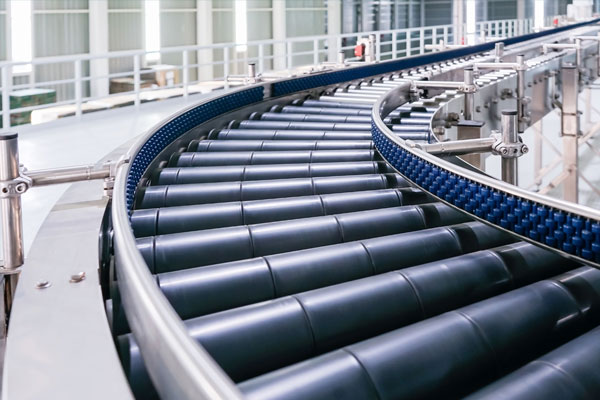

Roller Conveyors
Utilize rollers to move items along a track, ideal for heavier loads.
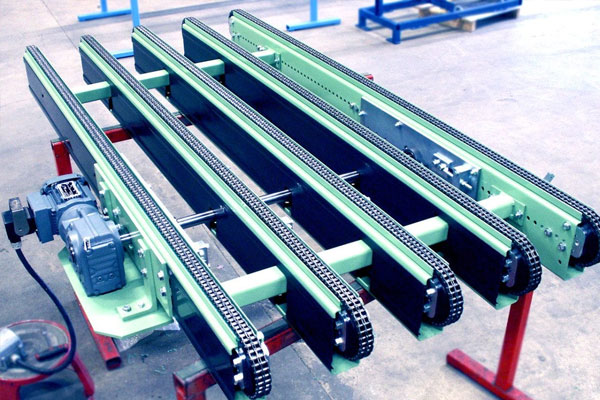

Chain Conveyors
Employ chains to transport materials more robustly.
Safety Equipment
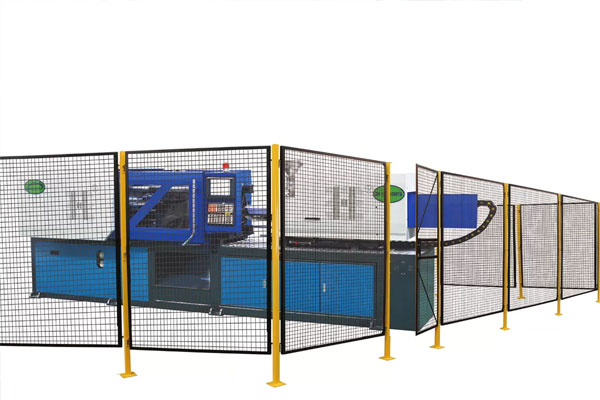

Guards and Shields
Protect workers from moving parts and hazardous areas.

Emergency Stop Buttons
Allow for quick machinery shutdown in emergencies.
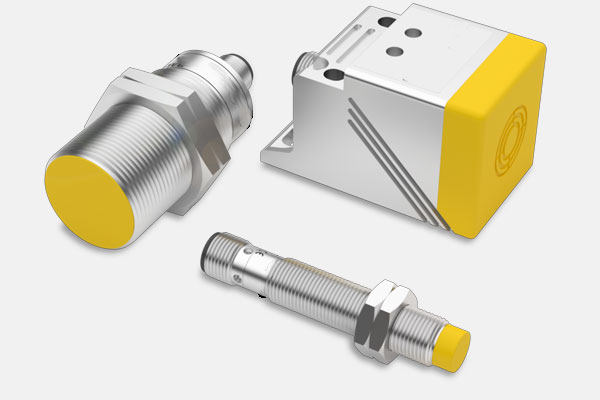
Safety Sensors
Detect unsafe conditions and automatically stop machinery.
Maintenance and Repair Parts
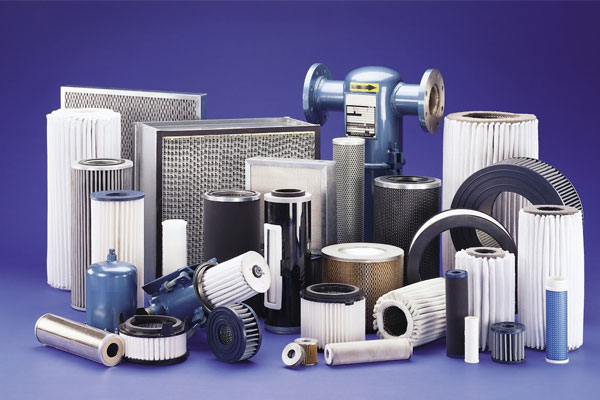

Filters
Remove contaminants from fluids or air in industrial systems.
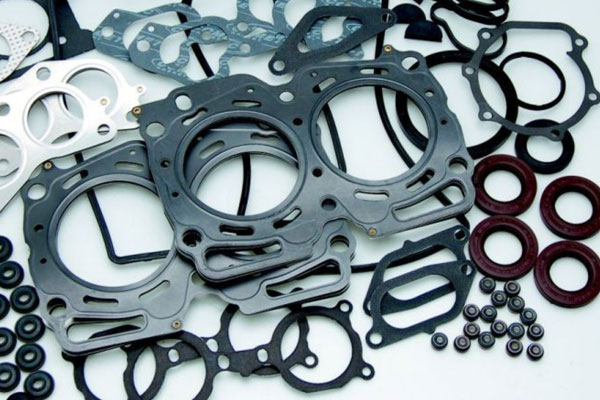

Seals and Gaskets
Prevent leaks in pipes, pumps, and other components.
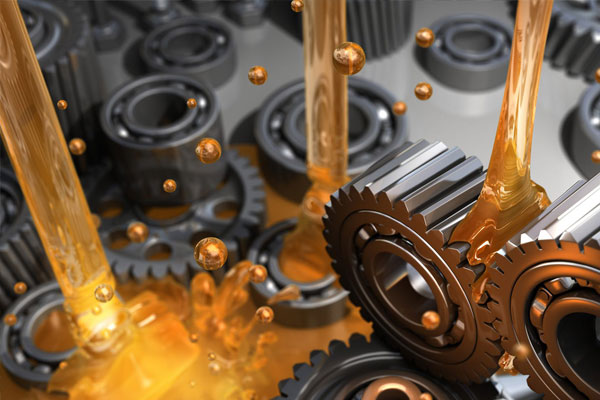

Lubricants
Reduce friction between moving parts and extend machinery life.
