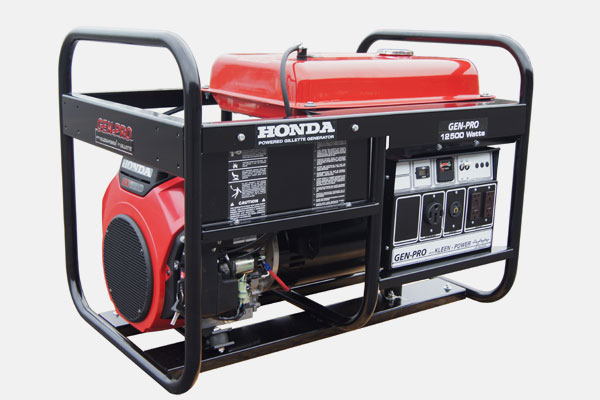
Portable Generators
Description: Compact and lightweight generators that are easy to transport.
Fuel Type: Typically powered by gasoline, propane, or diesel.
Applications: Ideal for outdoor activities, camping, and providing emergency backup power for homes.
Features:
- Outlets for connecting devices.
- Limited power output, generally ranging from 1,000 to 10,000 watts.
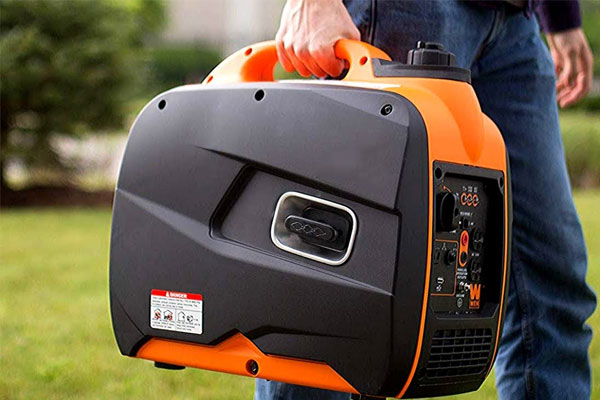


Inverter Generators
Description: Advanced portable generators that produce clean, stable power.
Fuel Type: Often powered by gasoline or propane.
Applications: Perfect for sensitive electronics like laptops and smartphones, as they deliver stable voltage.
Features:
- Lightweight design and quieter operation.
- Capability to connect multiple units for increased power output.
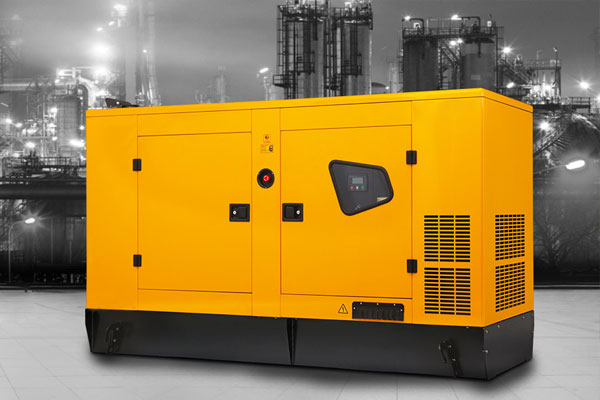
Standby Generators
Description: Permanently installed generators that automatically provide backup power during outages.
Fuel Type: Commonly powered by natural gas or propane.
Applications: Used in homes, businesses, and critical facilities that require uninterrupted power.
Features:
- Automatic transfer switch (ATS) for seamless switching during power loss.
- Larger power output, often exceeding 20,000 watts.
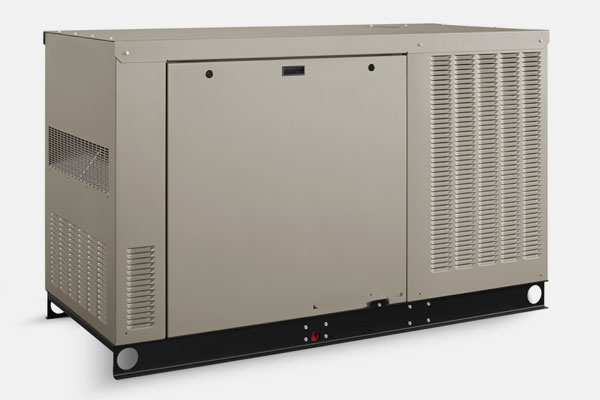
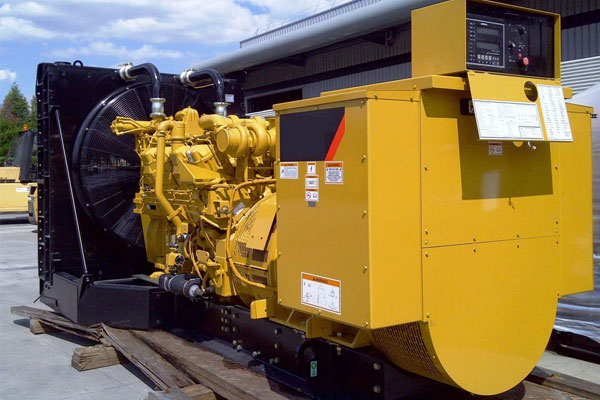


Industrial Generators
Description: Heavy-duty generators designed for large-scale power requirements.
Fuel Type: Can be powered by diesel, natural gas, or biofuels.
Applications: Utilized in construction sites, factories, and during natural disasters for reliable power.
Features:
- High power output (up to several megawatts).
- Durability and robustness suited for harsh environments.
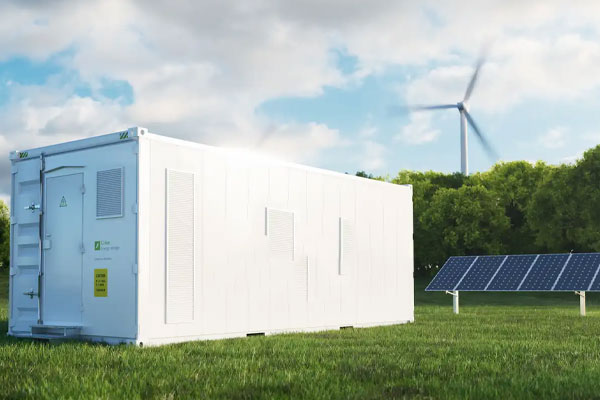
Renewable Energy Generators
Description: Generators that harness energy from renewable sources.
Types:
- Wind Generators: Convert wind energy into electricity.
- Solar Generators: Use solar panels to generate electricity.
Applications: Ideal for off-grid living, remote locations, and reducing carbon footprint.

Key Components of Generators
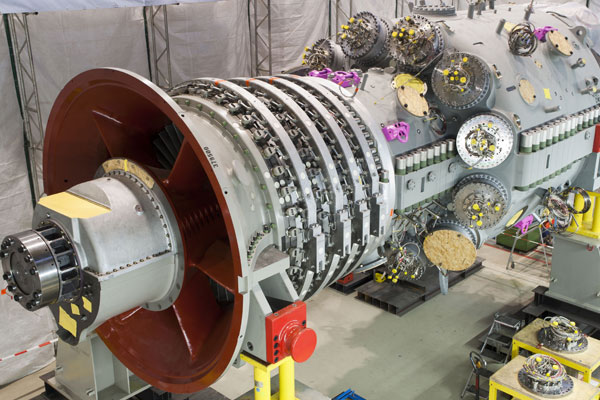
Engine: Converts fuel into mechanical energy, which drives the generator.
Alternator: Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, generating electricity.
Fuel System: Comprises the fuel tank, pump, and lines that supply fuel to the engine.
Cooling System: Maintains optimal operating temperatures, often using a radiator and fan.
Exhaust System: Directs exhaust gases away from the engine and minimizes noise.
Control Panel: Provides monitoring and control functions, including the ability to start and stop the generator.
Battery: Powers the starter and control systems.
Voltage Regulator: Ensures a consistent voltage output.
Applications of Generators
Residential: Provides backup power during outages for homes, powering essential appliances and systems.
Commercial: Supplies power for businesses, especially during emergencies, ensuring operational continuity.
Construction: Powers tools and machinery on job sites where grid power is unavailable.
Events: Supplies electricity for outdoor events, concerts, and festivals.
Emergency Services: Critical for hospitals, emergency response units, and disaster recovery efforts.

